Email file formats determine how messages transfer between platforms and preserve metadata. The choice between EML and MSG impacts compatibility, workflow efficiency, and data integrity. Microsoft Outlook users encounter MSG files, while cross-platform environments favor EML for universal accessibility.
Consider an IT team migrating emails between systems. Choosing the wrong format strips metadata and breaks attachments. Understanding these formats prevents costly errors and ensures smooth email management.
Key takeaways
- EML uses open standards (RFC 5322) for cross-platform compatibility
- MSG is Microsoft proprietary, preserving Outlook-specific metadata
- Choose EML for archiving and cross-platform sharing
- Choose MSG for Outlook workflows requiring full metadata fidelity
- Conversion risks include metadata loss and feature incompatibility
What Is the EML File Format?
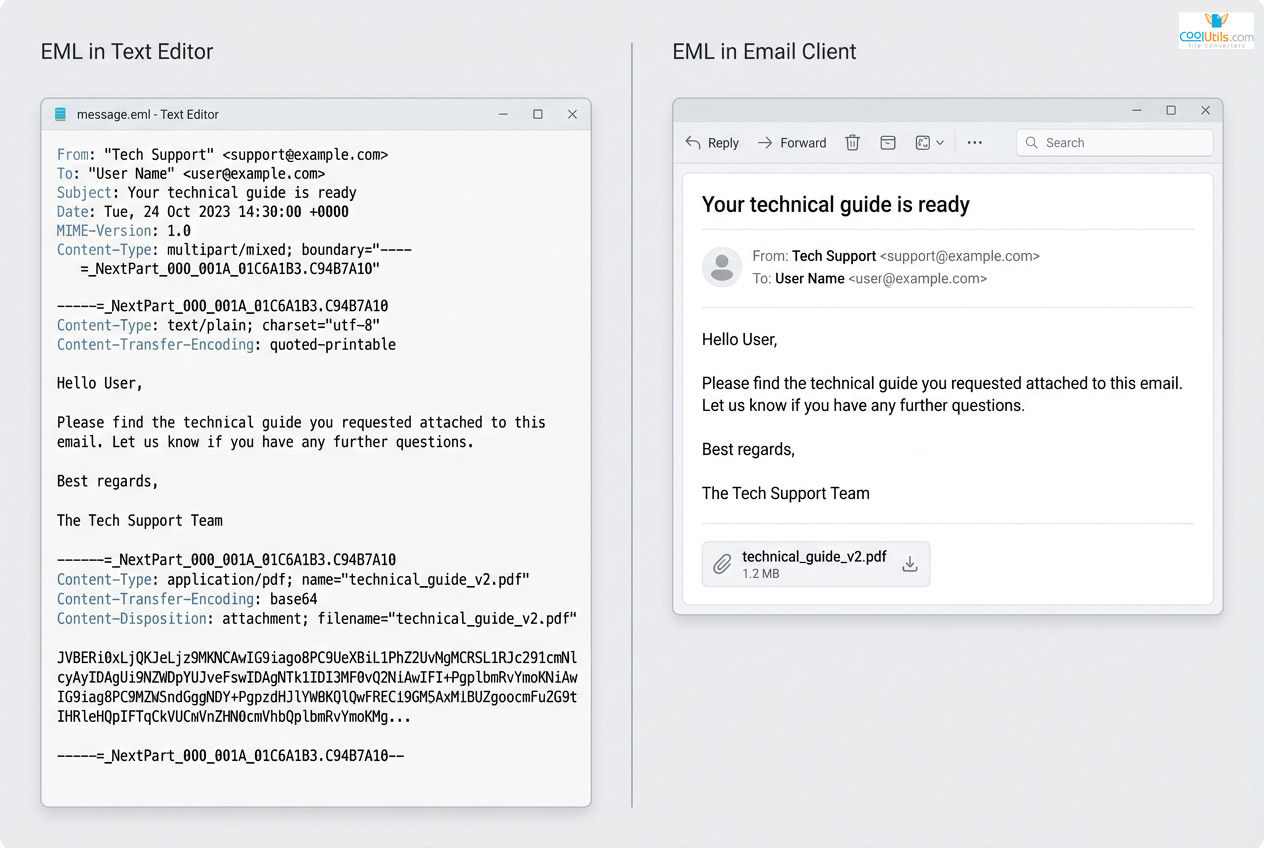
The EML file format stores email messages as plain text files following open internet standards RFC 822, RFC 2822, and RFC 5322. This format maintains universal compatibility across email clients and operating systems, capturing complete messages including headers, body content, and attachments using MIME encoding.
Mozilla Thunderbird, Apple Mail, and Windows Live Mail support EML natively. The text-based structure allows inspection with basic text editors, revealing email headers and content encoding without specialized software. This transparency makes EML valuable for archiving and debugging.
Open standard foundation ensures EML files remain accessible regardless of specific email client software. Organizations eliminate vendor lock-in while maintaining message integrity, with format longevity outlasting proprietary alternatives.
Key Characteristics and Components of EML Files
EML files follow predictable structure separating metadata from content. Files begin with email headers containing sender, recipient, subject, date, and routing information using standardized field names.
Message body follows headers, containing plain text, HTML, or both in multipart format. Attachments encode as MIME parts using Base64. This single-file approach keeps components together while maintaining text readability.
| From: [email protected]: [email protected]: Project UpdateDate: Mon, 22 Dec 2025 10:30:00 +0000MIME-Version: 1.0Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary=”boundary123″ –boundary123Content-Type: text/plain; charset=”utf-8″ Message body content here. –boundary123Content-Type: application/pdf; name=”report.pdf”Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64 [Base64 encoded attachment data]–boundary123– |
Essential components include:
- Headers storing metadata
- Body containing text/HTML
- Attachments encoded in MIME parts
- Boundaries separating content sections
- Character encoding supporting international text
Benefits and Advantages of the EML Format
Cross-platform compatibility represents EML’s primary strength. Files open correctly on Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile platforms without conversion, making EML preferred for sharing across systems.
Text-based structure simplifies long-term archiving. Unlike binary formats requiring specific software versions, EML files remain readable with text editors decades later. Compliance teams value this transparency for legal holds.
Common applications include email migration between clients, creating portable archives, sharing messages across organizations, and maintaining compliance records. Format simplicity suits scenarios requiring maximum compatibility.
What Is the MSG File Format?
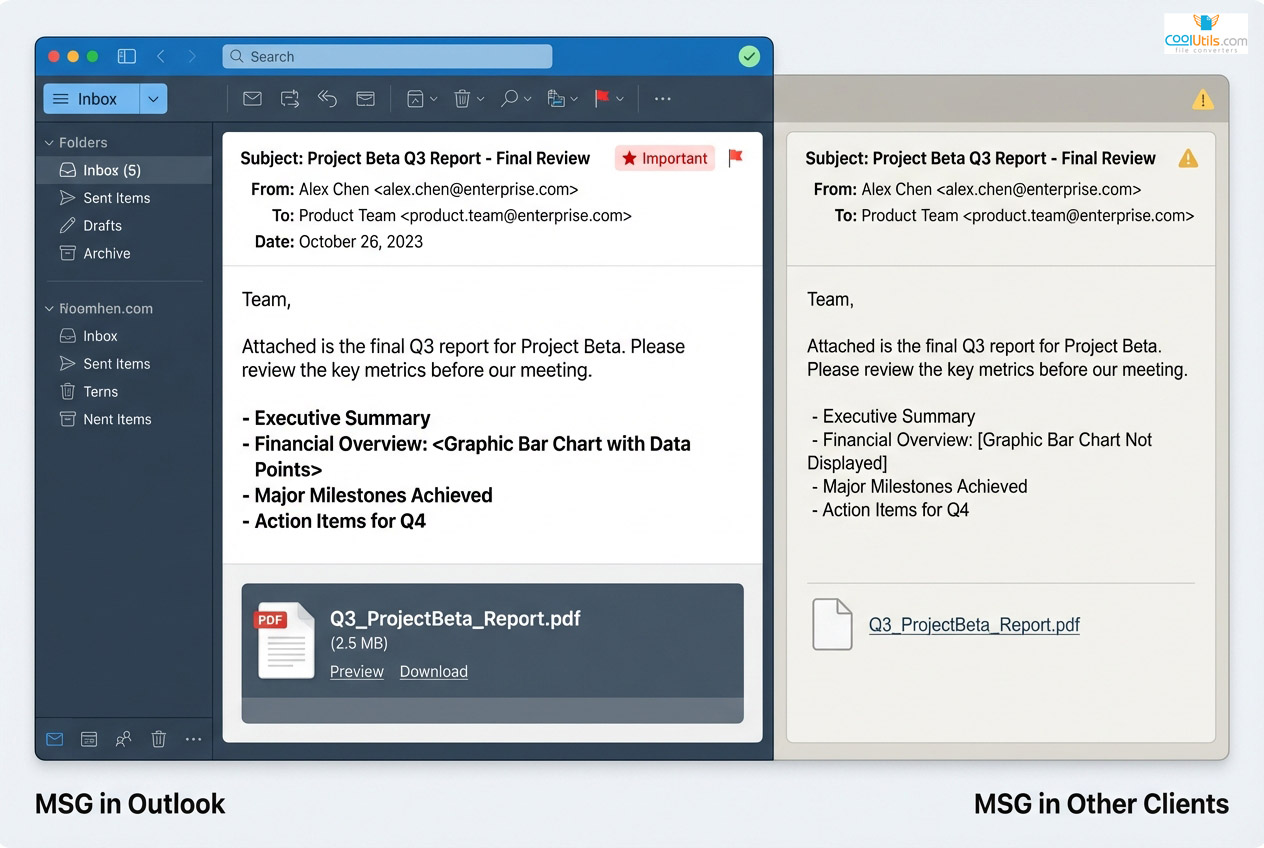
MSG serves as Microsoft’s proprietary format for storing Outlook email messages. Built on OLE Compound File structure, MSG files preserve Outlook-specific metadata beyond standard headers. This binary format integrates with Microsoft Exchange, maintaining features like message flags, categories, custom properties, and RTF formatting.
MSG files excel within Microsoft ecosystems where full Outlook functionality matters. The format stores email content plus calendar items, tasks, and contacts. This ensures perfect fidelity transferring data between Outlook installations.
Unlike open standards, MSG prioritizes feature completeness over universal compatibility. Organizations using Microsoft tools benefit from this design, while mixed environments face compatibility challenges.
Features and Structure of MSG Files
MSG files use OLE Compound File Binary Format, organizing data in hierarchical streams. This allows Outlook to store multiple data types within single files, including RTF formatting, embedded objects, and custom properties.
Outlook-specific metadata includes:
- Message flags: read/unread, follow-up, importance markers
- Categories for organization and filtering
- Custom properties and Extended MAPI fields
- RTF formatting beyond basic HTML
- Delivery receipts and read confirmations
- Conversation tracking for thread management
Binary structure stores each component in separate streams. Headers occupy one stream, body content another, and attachments exist as embedded sub-files. This enables Outlook to access specific components without loading entire messages.
MSG format preserves Exchange Server properties generic formats cannot represent, including server-side rules, retention policies, and compliance tags critical for enterprise management.
Benefits and Advantages of the MSG Format
Maximum fidelity within Microsoft environments represents MSG’s core advantage. When both parties use Outlook, MSG files transfer perfectly with zero data loss. Custom formatting, embedded objects, and Outlook-specific features survive intact.
Enterprise workflows benefit from Exchange integration. MSG files maintain server-side properties, retention tags, and compliance markers essential for regulated industries. eDiscovery tools designed for Microsoft environments parse MSG natively.
The format supports advanced Outlook features like voting buttons, meeting requests, and task assignments. These objects require MSG format to function properly when shared outside live Exchange connections.
MSG excels in internal Outlook communication, Exchange migrations, legal discovery in Microsoft organizations, and archiving with full metadata preservation.
EML vs MSG: Head-to-Head Comparison
Understanding practical differences between EML and MSG requires examining real-world email management tasks. Both store complete messages but use fundamentally different approaches.
| Attribute | EML | MSG |
| Standard | Open (RFC 5322) | Proprietary (Microsoft) |
| Structure | Plain text with MIME | Binary OLE Compound File |
| Native Support | Thunderbird, Apple Mail, Windows Live Mail | Microsoft Outlook, Exchange |
| Cross-Platform | Excellent (Windows/macOS/Linux) | Limited (primarily Windows) |
| Metadata | Standard email headers | Extended Outlook properties |
| File Size | Typically smaller for text | Smaller for large attachments |
| Long-term Storage | Excellent archival format | Dependent on Microsoft support |
The fundamental distinction: EML prioritizes universal compatibility through open standards, while MSG optimizes for feature completeness within Microsoft ecosystems.
Compatibility Across Email Clients
Email client support varies dramatically. Thunderbird and Apple Mail handle EML natively, displaying messages immediately. Windows Live Mail and Linux applications recognize EML directly.
Microsoft Outlook supports both formats differently. Outlook opens EML through import functions, converting to internal format. MSG files open natively with full functionality.
Gmail web interface treats both as attachment previews rather than native messages. Users can view basic content but cannot interact with messages as full email objects.
Thunderbird provides native EML support; MSG requires third-party extensions. Apple Mail supports EML natively with limited MSG viewing. Outlook natively handles MSG with EML import available.
Cross-Platform Considerations
Platform support determines format suitability. EML files work identically across Windows, macOS, and Linux systems. Users save EML on Windows, transfer to macOS, and open in Apple Mail without conversion.
MSG shows strong Windows bias. While Outlook runs on macOS, other platform-native clients cannot open MSG directly. Linux users face significant barriers—most applications require third-party conversion tools.
Mobile platforms present additional challenges. iOS and Android applications generally handle EML attachments better than MSG files.

Security Considerations for Email Files
Both formats carry security risks through malicious attachments or embedded content. EML’s text-based structure allows straightforward antivirus scanning. Security tools parse MIME boundaries and extract attachments without complex format knowledge.
MSG files require OLE-aware security scanning. Binary structure can obscure malicious payloads within compound streams.
Security best practices include scanning files with updated antivirus before opening, using sandboxed environments for unknown sources, disabling automatic macro execution, verifying sender authenticity, maintaining updated email clients, and training users to recognize phishing attempts.

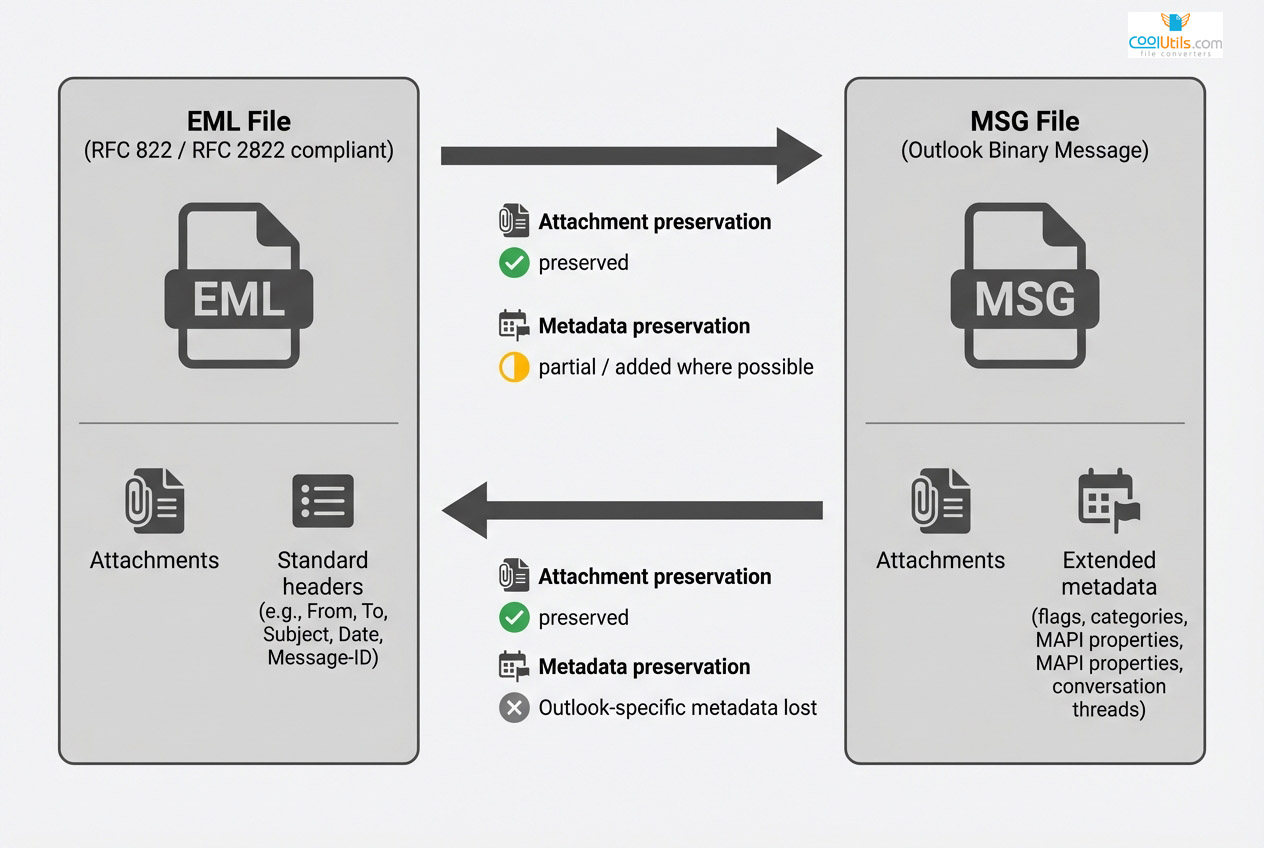
Converting Between Formats: Practical Methods
Format conversion becomes necessary when migrating between email systems, archiving messages, or sharing across platforms. The process must preserve content, attachments, and metadata where possible. However, information loss occurs translating between EML’s open structure and MSG’s proprietary format.
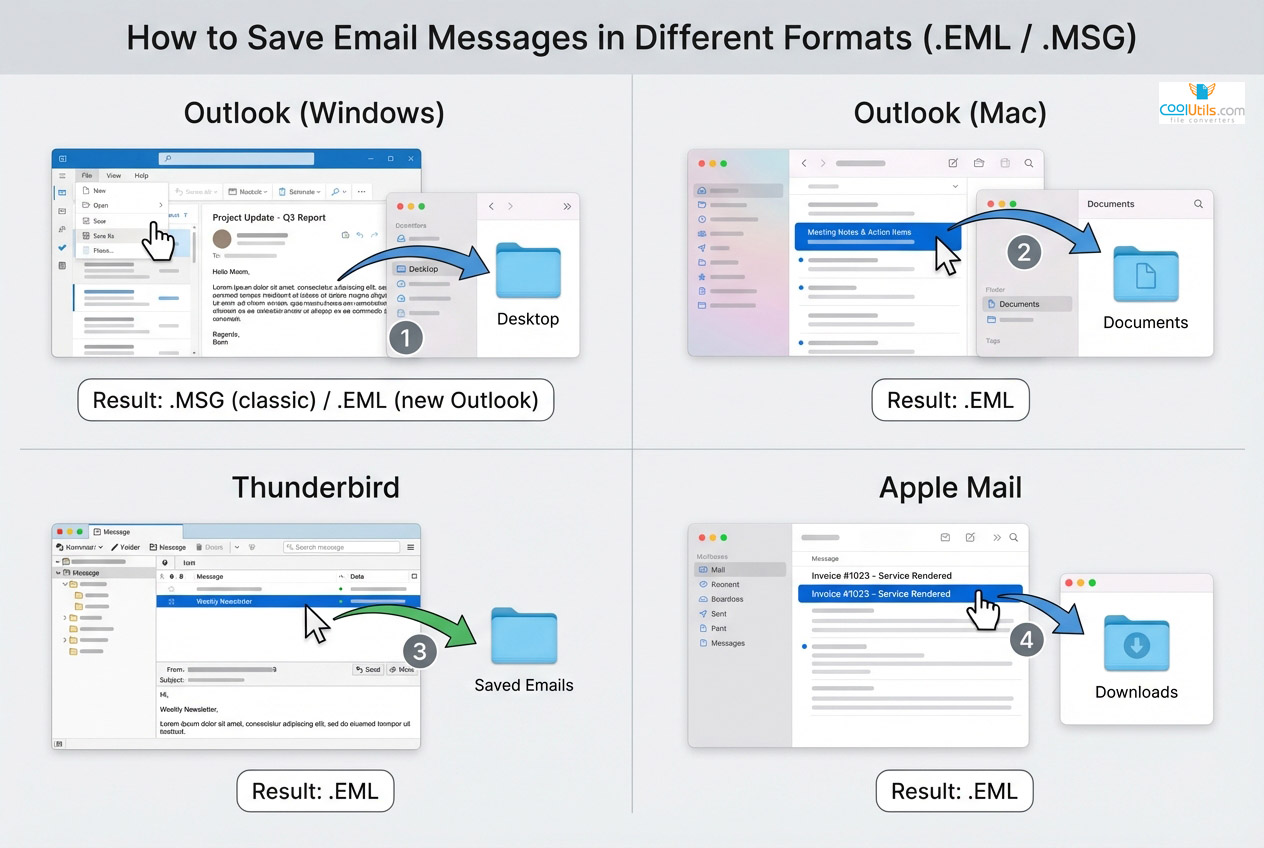
How to Save Email Messages in Different Formats
Microsoft Outlook behavior varies by version. Classic Outlook for Windows saves messages as MSG by default through drag-and-drop or “Save As” function. New Outlook for Windows changed this behavior, now saving as EML when dragging to file system. Outlook for Mac natively exports to EML format through drag-and-drop. Native EML support in “Save As” menu remains limited across versions.
Thunderbird exports EML natively through drag-and-drop. Users drag messages to file system folders, automatically creating EML files. Thunderbird lacks native MSG export—third-party extensions fill this gap.
Apple Mail handles EML export through drag-and-drop. Users drag messages from Mail to Finder, creating EML files. Apple Mail cannot create MSG natively.
Gmail downloads typically arrive as EML. Gmail Takeout exports mailboxes as MBOX format containing EML-structured messages.
Converting MSG to EML
MSG to EML conversion preserves basic structure while potentially losing Outlook-specific metadata. The process works well for standard messages but may strip custom properties and advanced formatting.
Manual conversion through Outlook: Open MSG file, select File ? Save As. Note that Classic Outlook for Windows defaults to MSG format; newer Outlook versions may offer EML export. Verify attachments survived conversion.
Dedicated conversion tools offer batch processing. Software handles hundreds of MSG files simultaneously, preserving headers and attachments.
Online services provide quick solutions for occasional needs. Privacy concerns limit this approach for sensitive email.
Conversion considerations:
- Outlook categories may not transfer
- Custom MAPI properties will be lost
- RTF formatting converts to HTML approximation
- Follow-up flags disappear
- Server-side rules are stripped

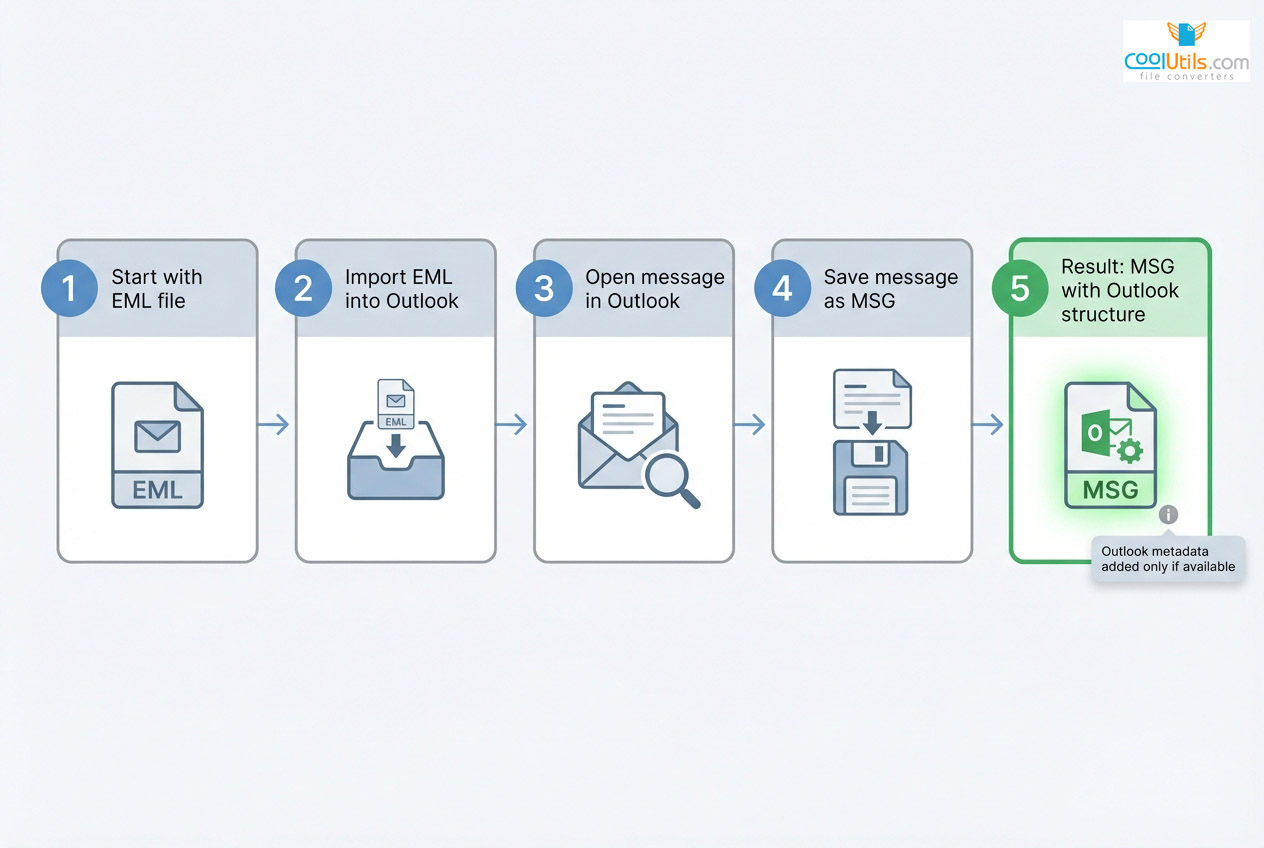
Converting EML to MSG
EML to MSG conversion brings open-format messages into Outlook’s structure. Process adds MSG-specific fields but cannot create Outlook metadata absent from original EML.
Import method: Open Outlook, drag EML file into folder or use Import/Export, select EML for import, save message as MSG, verify content displays correctly.
Batch conversion software handles large EML collections efficiently, converting thousands while maintaining folder structure.
Challenges include HTML formatting rendering differently, character encoding issues, inline images detaching, MIME structure altering attachment behavior, and custom headers being dropped.
Using Native Email Client Features for Conversion
Email clients provide varying built-in support. Classic Outlook for Windows handles Import/Export wizard for multiple formats, drag-and-drop for MSG files, and native MSG creation through “Save As.” New Outlook for Windows changed drag-and-drop behavior to create EML files instead of MSG.
Thunderbird offers native EML export through drag-and-drop, ImportExportTools add-on for extended support, and MBOX import/export for bulk operations.
Apple Mail provides drag-and-drop for automatic EML creation, mailbox export creating MBOX format, and AppleScript automation for batch operations.
Native features work for occasional conversions. Organizations facing regular conversion needs benefit from dedicated tools handling edge cases and preserving more metadata.

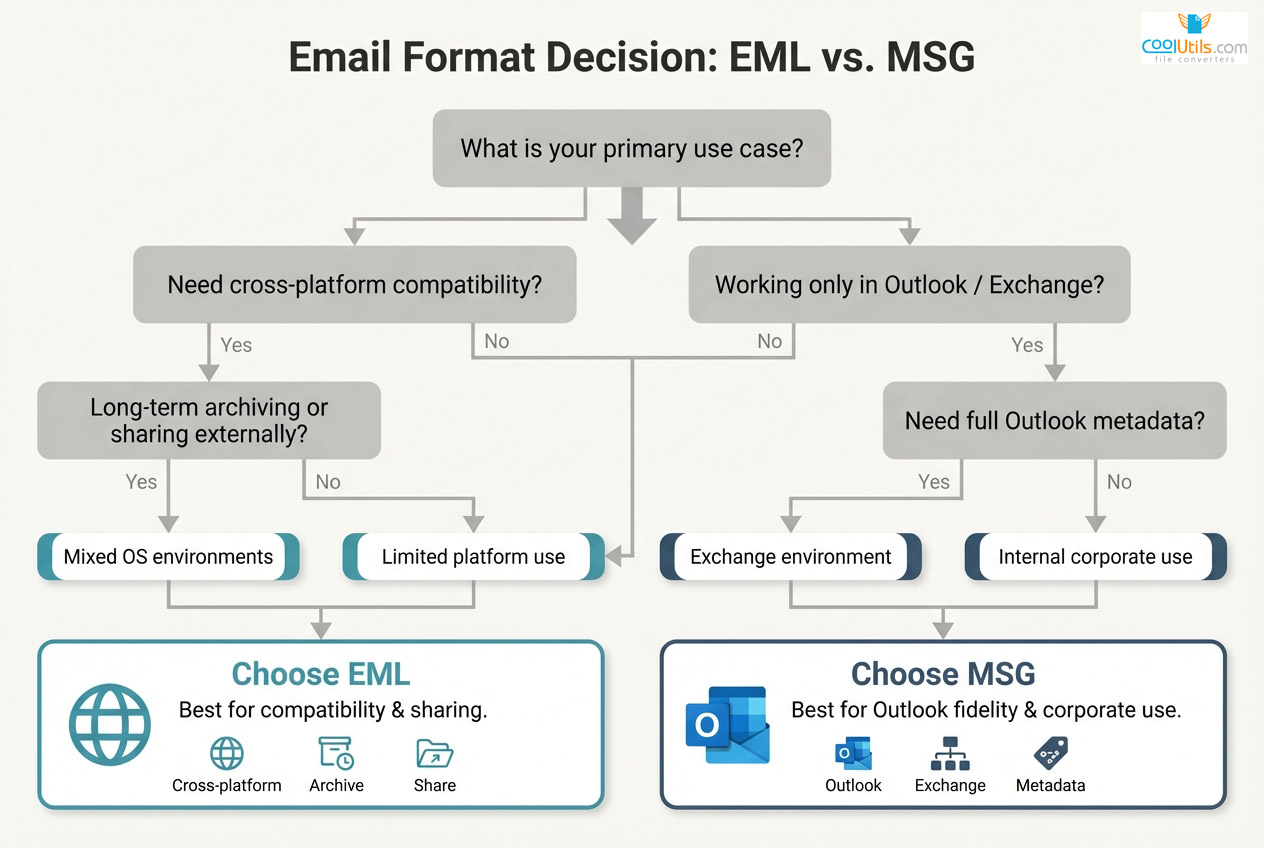
Choosing the Right Format for Your Needs
Format selection impacts workflow efficiency, collaboration effectiveness, and long-term data management. The decision requires evaluating current infrastructure, future migration plans, and external communication requirements.
Choose EML for:
- Cross-platform email client compatibility
- Sharing with external organizations
- Long-term archiving and compliance
- Mixed-OS environments (Windows/macOS/Linux)
- Platform migration flexibility
Choose MSG for:
- Exclusive Microsoft Outlook/Exchange environments
- Full Outlook metadata preservation
- Windows-centric organizations
- eDiscovery with Microsoft-focused tools
- Internal Outlook-only workflows
Mixed environments present challenges. Organizations using both Outlook and other clients must balance compatibility against features. Many adopt hybrid approaches: EML for external communication and archives, MSG for internal Outlook workflows.
Decision scenarios vary. Legal archiving benefits from EML standardization—law firms collecting evidence from diverse sources ensure consistent accessibility regardless of platform. Enterprise migrations need formats supporting smooth transitions. EML provides universal bridge format, though MSG better preserves Exchange properties temporarily. Collaboration scenarios require cross-platform functionality. EML eliminates compatibility barriers.
Future Outlook for Email File Formats
Email storage evolves toward cloud-based solutions and web interfaces, potentially reducing reliance on local file formats. Gmail, Outlook.com, and similar services store messages in proprietary databases rather than discrete files. This shift diminishes the role of both EML and MSG for daily management.
However, offline access requirements and archival needs ensure continued format relevance. Compliance regulations often mandate local email archives in standardized formats. EML’s open standard structure positions it well for long-term preservation regardless of technology changes.
Emerging trends include:
- Cloud migration reducing local storage while increasing export/import needs
- Compliance requirements driving format-independent archiving
- API-based email access supplementing file-based management
- Container formats like MBOX gaining traction for bulk storage
- Growing open standards pressure as organizations seek vendor independence
- Mobile-first clients prioritizing universal format support
Microsoft continues evolving Outlook and Exchange, potentially affecting MSG format relevance. As Microsoft embraces cloud services and cross-platform support, rigid adherence to proprietary formats may soften. Recent Outlook versions show improved open standard support.
Long-term archival strategies should prioritize format independence. EML’s text-based structure and open foundation provide better longevity guarantees than binary proprietary formats.

Frequently Asked Questions About EML and MSG Files
Email file format questions arise during migrations and archiving projects. Understanding common issues prevents data loss and workflow disruptions. Below are answers to frequently asked questions about EML and MSG formats.
What is the difference between MSG and EML?
EML is an open, plain-text MIME format based on internet RFCs, widely supported across clients; MSG is Microsoft’s proprietary OLE format, native to Outlook, preserving Outlook-specific metadata.
What is an EML file?
An EML file stores a full email (headers, body, attachments) as a text message using MIME, adhering to RFC 5322 for broad compatibility and archiving.
What is an MSG file?
An MSG file is a Microsoft Outlook message in OLE Compound format, retaining rich Outlook data such as flags, categories, and custom properties.
Is it better to save as EML or MSG?
Choose EML for cross-platform sharing and long-term archiving; choose MSG for Outlook-to-Outlook workflows where full Outlook metadata fidelity is critical.
How do I convert from EML to MSG?
Import EML into Outlook and save as MSG, or use a reputable converter for batch jobs, ensuring attachment and metadata preservation settings are enabled.
How do I convert MSG to EML?
Open MSG in Outlook and export/save as EML (or use a converter/online tool). Verify headers, inline images, and attachment integrity after conversion.
Which email clients support EML and which support MSG?
Thunderbird and Apple Mail natively support EML; Outlook natively supports MSG and can import EML. Gmail web interface offers attachment preview for both formats but does not open them as native messages.
What security considerations apply to EML vs MSG?
Both can contain malware via attachments or embedded content. Scan files, use sandboxed viewers, and avoid enabling active content.
What happens to attachments when converting between EML and MSG?
Attachments usually transfer, but metadata or inline rendering can change. Always verify filenames, content types, and inline images post-conversion.
How do I save an original email as .eml or .msg?
Classic Outlook for Windows saves as MSG by default via drag-and-drop or “Save As”; New Outlook for Windows saves as EML via drag-and-drop. In Apple Mail/Thunderbird, use Save As/Export or drag-and-drop to create EML files. Outlook for Mac creates EML files through drag-and-drop.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- MSG files won’t open outside Outlook: Install MSG viewer application or convert to EML using converter software. Many free MSG viewers exist for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- EML formatting looks broken: Check character encoding settings in receiving email client. Try opening in different client to isolate issue.
- Attachments missing after conversion: Verify conversion tool settings preserve attachments. Re-convert with different tool if necessary.
- Conversion errors with large files: Split large archives into smaller batches. Increase system memory for conversion tool.
- Email client won’t import files: Verify format compatibility with target client version. Update email client to latest version.
- Character encoding displaying incorrectly: Examine email headers for charset specification. Configure email client to use UTF-8 encoding.
Conclusion
EML and MSG formats serve distinct purposes in email management. EML provides universal compatibility and long-term archival stability through open standards, while MSG delivers maximum feature preservation within Microsoft Outlook environments. The right choice depends on specific workflow requirements, platform infrastructure, and collaboration needs.
Organizations should evaluate format decisions based on current platform mix, future migration possibilities, and external communication patterns. Mixed environments benefit from understanding both formats and maintaining conversion capabilities. EML excels in cross-platform scenarios and archiving, while MSG optimizes for Outlook-specific features and Exchange integration.